Terms and Concepts
Database
Databases are the core data storage structures in XINA. A database essentially defines a MySQL table, with additional features managed by the XINA server system.
Each database is defined by a set of fields, which specify the columns of the table. Fields are primarily defined by:
- Name, unique to the field in the database
- Static data type
- Whether a value must be provided by each record (an empty value being null)
A single unit of data in a database is a record, corresponding to a row of the table. Each record contains a value for each field of the database.
Structural database changes (adding / changing / removing fields) are very slow (hours to days for very large databases) so initial time investment to optimize database requirements is worthwhile.
Group
Databases in XINA are organized into a heirarchical structure of groups, which can each contain any number of groups and databases. For example:
- The
modelgroup contains ajournaldatabase anddatagroup - The
datagroup contains ahousekeepingdatabase andsciencedatabase

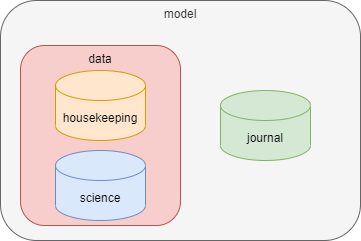
A dot notation is used to reference groups and databases. For example, moma.data.science refers to the science database in the above configuration.
