User Guide
User Guide for the Data Viewer application. Each mission has their own version to document mission specific functionality.
- Overview
- Installation
- DraMS Mnemonic Plot Tool
- Starting the app
- Mnemonic Database
- Export Data
- Clear Cached Data
- Change the refresh rate
- Chart Tips
- Quick Graph
- Open a new viewer
- Create Tabular or Graph Viewer
- OCI Viewers
- OCI Step-by-step Instructions
- ADC Sweep
- Touch Sensitivity Test
- ADC Output Phase Tuning
- RG Sweeps
- EMI Testing
- DDC Raw Capture
- DDC Scope Capture
- Data Viewer Usage in PACE I&T
Overview
The Data Viewer provides the following features:
- View data in real-time. Supports TCP or reading from a file.
- Load archives to post-process data. Supports CCSDS or 699 packets. Other formats can be easily supported.
- Generic displays (viewers) of telemetry data:
- Tabular view
- Time series plots
- Packet statistics
- Event log
- Data rate
- Raw packets as hex
- Custom viewers to meet a mission's needs
- Generic and per mission settings
- Display science data and housekeeping telemetry data together
- Save and load viewer configurations
- Multiple models per mission to support per model configuration
- Supports interpretation of the ITOS and ASIST mnemonic definition formats
Any bug reports, feature requests, or general questions can be sent to Bradley Tse via email: bradley.c.tse@nasa.gov or messaged directly over NASA's Teams instance.
Architecture
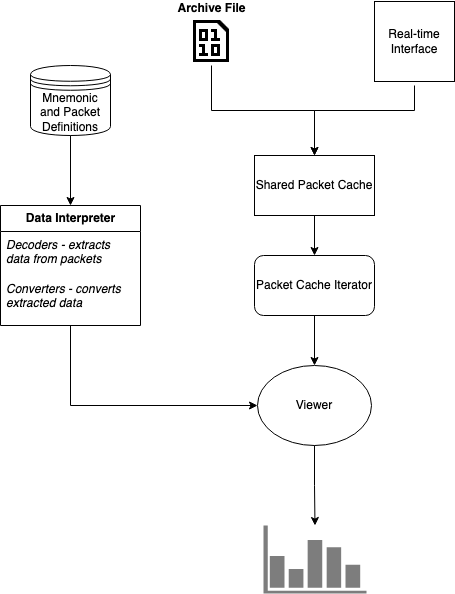
Installation
The Data Viewer is actively supported on Mac OS and Linux. Windows support can be provided if required.
Mac OS
Mac OS versions are distributed in dmg format. Contained within the dmg is a single .app which can be placed anywhere on your machine and then run. The .app contains all required dependencies. The standard install location is your /Applications directory but can be run from anywhere.
Linux
The Linux version is distributed as an AppImage, which closely emulates how the Mac OS apps work; all dependencies are contained within the AppImage. This makes it easy to distribute and run. The user or sys admin does not need to manage dependencies. The AppImage can be run from any directory.
gse directory
We use a separate "gse" repository for each mission to store released versions of the Data Viewer, config files, and other miscellaneous applications and items. For example, on OCI we have an ocigse Git repository that's maintained on the gs490v-gitlab GitLab. We use version control to sync across workstations and users.
The instructions to setup the gse directory is mission specific, but can generally be boiled down to:
- Acquire permissions to access the repository. Usually a NAMS request.
- Checkout the repository
- Perform initial one-time setup
The instructions to setup the ocigse directory are maintained in the README.md of the repository: https://gs490v-gitlab.ndc.nasa.gov/497_OCI/OCI_XINA
DraMS Mnemonic Plot Tool
The Mnemonic Plot Tool is useful for looking at mnemonic data, like voltages and temperatures, over time.
Link to tool: drams.xina.io/tool/mn
Link to tutorial video: Click here
Link to PDF presentation: Click here
Link to PowerPoint file: Click here
Starting the app
When first opening the application, you may be prompted with various dialogs, all of which can be closed.
The main window of the application looks like
If this window is closed, the whole application will be shut down.
On some OSes, the menus will be accessible from this window. On others, the menus may be displayed along the top bar.
Real-time
To start viewing data in real-time:
Load from archive
You can also load and view data from archives. This can be done in a number of different ways:
File --> TID Explorer
This will open up a new window that displays a tree view of your root data directory which is configured in your ~/.699config.INI file.
File --> Open Archive
Opens up a standard file dialog. Any file can be opened and parsed, so it's up to the user to select a valid archive file.
File --> Open TID
Opens up a file dialog to select a Test Directory. The test directory must match an expected formaat. TBD
File --> Open next TID
Opens up the next TID. The test data directory needs to follow a standard structure. TBD
File --> Open next TID
Opens up the previous TID. The test data directory needs to follow a standard structure. TBD
Mnemonic Database
When opening the application, the newest version of the mnemonic database is automatically loaded. You can manually load a different database with File --> Load database.
Export Data
File --> Export HK Data...
This will export ALL mnemonics for all cached data to your home directory. This feature has not been actively maintained and may not function as expected.
Clear Cached Data
A configurable amount of packets are cached in memory. To clear out all cached data: Data Viewers --> Clear all data
Change the refresh rate
Data Viewers --> Set Viewer Refresh Rate
Chart Tips
TODO
Quick Graph
You can quickly graph telemetry data over time.
Data Viewers --> Quick Graph
Open a new viewer
This method is used for opening up standard mission independent viewers:
Data Viewers --> Viewer Finder
Missions specific viewers can be opened up directly from the Data Viewers menu.
The viewers listed in the last section of the Data Viewers menu are the currently open viewers. Selecting from this list will bring it to the front.
Create Tabular or Graph Viewer
Data Viewers --> Make HK Viewer
OCI Viewers
Instructions on how to use the various OCI viewers
DDC Raw
The DDC Raw Viewer is used to display the DDC Raw captures. The DDC Raw captures are used for examining the raw samples out of the ADC. This mode is used for various tests:
- Line Tune Dark
- ADC Sample Point sweep
- RG Mag sweep
- RG Low sweep
OCI Step-by-step Instructions
Step-by-step instructions to use the Data Viewer for various OCI tests
ADC Sweep
This page contains instructions on how to view the ADC Sweep data with the DDC Raw Viewer.
The ADC sweep is performed by capturing multiple DDC raw captures while stepping the ADC sample point, which is a combination of the ADC mux delay (fine steps) and ADC Clock offset (coarse steps). One or more DDC Raw Captures may be collected at each step, depending on how the ITOS proc is configured. The collection of all steps is an "ADC Sweep".
Setup
- Open the DDC Raw Viewer (bring to front an existing one or open a new one)
- Set the
CCD ID - Start ADC Sweep ITOS procedure
- The viewer will update when a complete DDC raw capture is received. A single raw capture may look something like:

The colored regions indicate the different parts of a "line". Each raw capture contains ~11 lines of data (dependent on various OCI settings). The "INFO" annotation indicates the start of a raw capture.
Sweep Finished
When the ADC Sweep is finished, you may see something like below. (The actual shape may vary depending on the environment and other variables)
Scroll down to view the charts titled ADC Tap and CDS SD Tap. These are the main charts we will be using to analyze the ADC Sweep data.
The ADC Tap chart displays the ADC Counts vs. ADC Sample Point, where ADC Sample Point (x-axis) is defined as:
ADC Sample Point = (ADC Clock Offset * 48) + Mux Delay
The ADC Clock Offset is also known as the coarse setting, Mux Delay as the fine setting.
The CDS SD Tap chart displays the standard deviation of the calculated CDS for the image pixels (green region) of the 11 lines per capture.
If no data is visible, you may need to rescale the chart. You can do this 1 of 3 ways: double click on the chart, right click and select "Reset zoom", or click on the number at the top right corner of the chart.
Below are a few other notes:
- There is one ADC Tap and CDS SD Tap chart per tap.
- You may uncheck the
Per Tap Vid/Ressetting to hide the leftmost chart - The
Sync Axessetting will keep all of the chart axis ranges in sync. If you wish to control each chart separately, set this toNone. - If you wish to auto scale the y-axes, check
y auto. This will immediately rescale the y-axes, and to any new data that arrives. A common trick is to check and then uncheck to immediately rescale all of the y-axes. Note that even withy autochecked, theSync Axessetting is still enforced which may cause unexpected behavior.
At the end of the ADC Sweep, you may see something like this:
The ADC Tap charts are used to determine the ADC sample point settings we want to use. How this decision is made is outside the scope of these instructions.
You may see a jump/discontinuity in the chart when going to the next coarse setting. This occurs because the actual timing delay is not continuous, but we treat and display the ADC sample point as continuous. In the below chart, you can see discontinuities at x=48 and x=96, which is where the coarse setting is incremented. This should be kept in mind when determining what sample point to use.
Exporting
- To export all of the ADC Tap charts as a single image, click the Export ADC Charts button.
- To export all of the CDS SD Tap charts as a single image, click the Export CDS SD Charts button.
- Each raw capture is automatically exported to disk. You can the export path in the status bar at the bottom of the window. Each raw capture is written to a single file. A corresponding hk file is exported containing relevant telemetry data for the raw capture. Unfortunately, we do not automatically group all of the raw captures for a complete ADC Sweep. You can determine this manually by using the timestamp in the filename. Zip up all relevant files for the ADC Sweep if further analysis is required.
Touch Sensitivity Test
This page contains instructions on how to use the Data Viewer during the touch sensitivity tests.
Setup
- Open 2 instances of the Stats Per Pixel vs. Time viewer. (or bring to front if already open)
- Set the
Stats Modeon one toSDand the other toAVG. Note: The window title displays theStat Modewhich can be used to differntiate the 2 instances. - For both configure the following settings:
-
Subtrack Dark:None -
HAM Side:Both -
Lines mode:All -
time win[s]:120 (or something reasonable)
Optional:
-
y-auto:check if you want the y-axis to auto scale to new data -
Sync Axes:If enabled, the axes across the charts will be kept in sync -
Series Names:Switch between pixel number and wavelength
Real-time operations:
- Click the Pause button if you want to stop auto-scrolling the x-axis to new data
- Click the Go Live button to resume auto-scrolling the x-axis to new data
- Set the
time win[s]to 0 to scale the x-axis to all data - If you zoom in on a chart, the x-axis auto-scrolling will be disabled if the most recent data is no longer visible on the chart. You can resume auto-scrolling by resetting the zoom or clicking the Go Live button.
No data?
The charts may need to be properly scaled. Double click to zoom out, or right click and select "Reset Zoom".
Exporting
You can export the charts as a single image by clicking on the Snap button.
Examples
ADC Output Phase Tuning
RG Sweeps
These instructions are for the Rg Mag and Rg Low sweeps.
EMI Testing
These instructions detail how to use the data viewer during EMI testing.
- Update to get the newest EMI window config
- Open a terminal
-
cd ocigse -
git pull - Close terminal
- On the bottom menu bar, click on
ocidataviewand select theOCI Data Viewerwindow.
-
At the top of this window is a menu bar. Select
Setup->Restore Windows -
Select
emiand click OK. This will load the 'emi' window configuration and may take up to a minute to reload the cached data. -
You can switch between the open viewers by clicking on the
ocidataviewin the menu bar and then selecting a viewer from the list. -
The 4 main viewers you will be using are:
- SSM Ch Stats vs. Time - AVG - Displays AVG counts for the whole scan per SSM channel.
- SSM Ch Stats vs. Time - SD - Displays SD for the whole scan per SSM channel.
- Stats Per Pixel vs. Time - AVG - Displays AVG counts for the whole scan per FPA pixel.
- Stats Per Pixel vs. Time - SD - Displays SD for the whole scan per FPA pixel.
Susceptibilities are more apparent in the SD variants; below is an example of what this may look like:
``DDC Raw Capture
Instructions to generate DDC Raw Capture images:
- File -> Open Archives -> Select archives to open. You may select more than one.
- Open DDC Raw viewer if not already open: Data Viewers -> DDC Raw
- Maximize the window
- Set settings on the right side:
- CCD ID: Red or BLUE
- Chart Height: 500
- Sync Axes: Both
- Show Regions: checked
- Line Window: 1
- Right click the "All Taps Video" chart's y-axis, set range [14500, 16500]
- Right click the "All Taps CDS" chart's y-axis, set range [-50, 500]
- If desired, right click on each chart and select "All series data points visible"
- All other settings can be left at the defaults
- Capture screenshot of whole window, except stop before the "All Taps Raw Samples" chart. Include the settings area on the right side.
- Repeat as needed for RED/BLUE
Below is an example screenshot:
DDC Scope Capture
The DDC Scope Mode Viewer is used to view and export the collected DDC Scope Capture data.
- File -> Open Archives -> Select archives to open. You may select more than one.
- Open DDC Scope Mode viewer if not already open: Data Viewers -> DDC Scope Mode
- Maximize the window
- Any scope captures will be parsed and loaded into the "Capture List"
- Under "Export Settings":
- If "Auto Export Raw CSV" is checked, the raw data will be auto exported to a CSV into ~/ocidata/scope_captures/
- If "Auto Export Retimed CSV" is checked, the retimed data will be auto exported to a CSV into ~/ocidata/scope_captures/
- If "Auto Export Charts" is checked, chart images will be automatically generated to ~/ocidata/scope_captures. The y-axis for these images are scaled for dark data. For light images, you will need to manually adjust the images and then click "Export Charts".
- The auto exported images are usually good enough for our functional tests. However, for special tests, such as performing scope captures with light, you will need to manually adjust the y-axis and export the charts by clicking "Export Charts".
Data Viewer Usage in PACE I&T
Overview
Usage of the Data Viewer in PACE I&T has changed since we no longer receive OCI science data in real-time. OCI Science File Archives are stored on-board PACE and downlinked at a later time. OCI HK and GSE data are still received in real-time.
A few updates to the Data Viewer and Science VMs have been made to accomadate for these changes.
We will be running 2 instances of the Data Viewer:
- One will be used to look at OCI HK and GSE data in real-time
- The other will be used to open OCI Science File Archives (which also contains OCI HK data)
In the bottom right of the VM, you will see 3 workspaces:
The Live workspace contains the Data Viewer that will receive OCI HK and GSE data in real-time from the FEDS. This instance of the Data Viewer works the same as in the OCI I&T environment.
The Playback workspace contains the Data Viewer that will be used to open and view OCI Science File Archives.
The GSE workspace contains an application that archives GSE data locally so it can be merged into the OCI Science File Archives so that OCI Science Data and GSE data can be viewed at the same time. You do not need to worry about this workspace.
Viewing OCI Science Data
To view OCI Science Data, first switch to the Playback workspace.
Open the Local Playback window:
You should see a window popup that looks like this:
Archive Index:
The Archive Index section on the right side displays the OCI Science File Archives that have been downlinked to the ground. You can click the Refresh button to refresh the list of archives. The list is also automatically refreshed the first time the Local Playback window is opened. This implies that the list is not automatically kept in sync with what archives have been downlinked.
You may click Load Selected Archive to immediately open the currently selected archive. Note: Using this method will not contain any GSE data.
Playback:
The Playback section on the left side is used for playing back time ranges of data. When you use this functionality, it will attempt to merge GSE and OCI data so that both are viewable at the same time.
Selecting an archive in the Archive Index list will automatically update the Start time input. A Duration can be selected to choose how much data will be viewed. The max duration is 10 minutes due to resource limitations.
NOTE: The Set to most recent is NOT aware of what data exists in the archives. It offsets from the system's current time, not the data.
Fast as possible should generally be left checked.
Once configured, click Start to initiate the playback. When the playback has finished, the Data Viewer will automatically load the archive.










